An Overview of Pediatric Malocclusion

Pediatric malocclusion is a dental deformity disease that affects many children in the United States. A small section of these cases may require an orthodontist's intervention to ensure they do not develop into severe dental issues.
Parents and guardians should understand the essence of pediatric malocclusion to ensure they receive early intervention since it improves the effectiveness of the corrective measures. Therefore, learn more with this overview of pediatric malocclusion to help you understand the dental disorder.
Definition
Pediatric malocclusion is a misalignment of the teeth in children, which can often occur either as an inherited trait or as the result of an injury. The severity of malocclusion can range from mild (slight misalignment of a few teeth) to severe (extensive misalignment of most or all teeth).
Effects
While the effects of pediatric malocclusion can vary depending on the severity of the misalignment, some common effects include difficulty chewing or biting food, speech impediments, and an increased risk of tooth decay and gum disease. In severe cases, malocclusion can lead to facial deformities and jaw joint problems.
Diagnosis
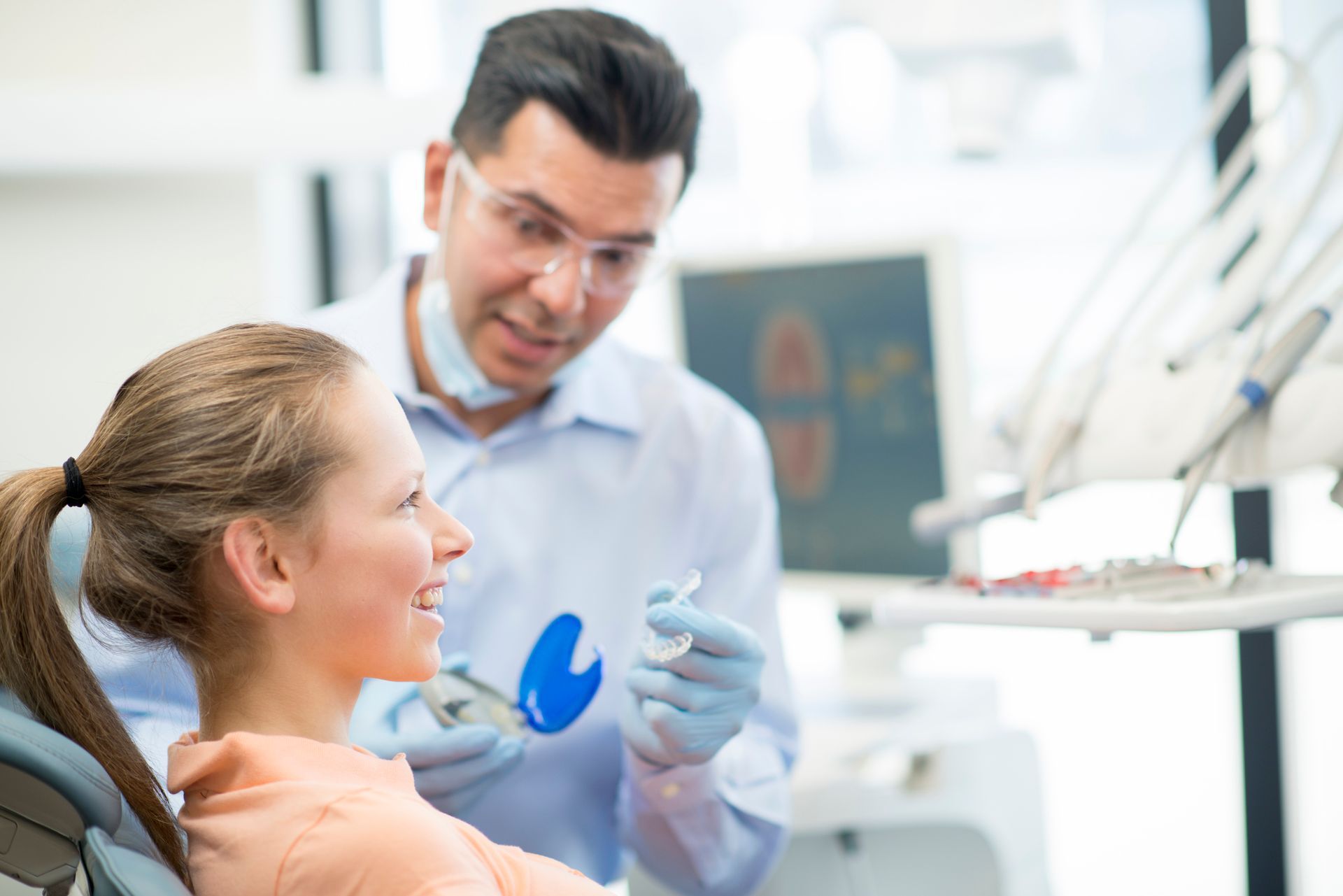
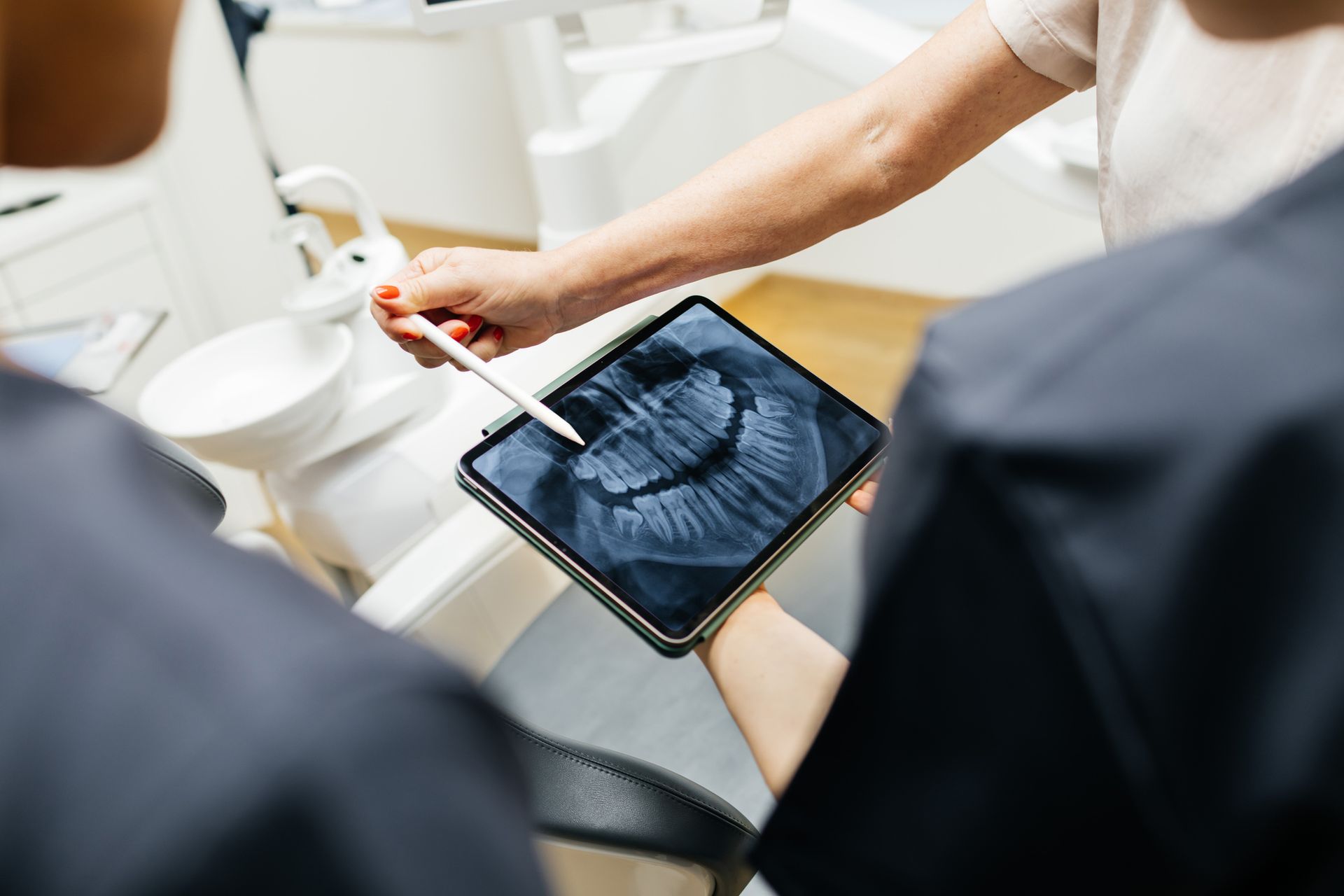
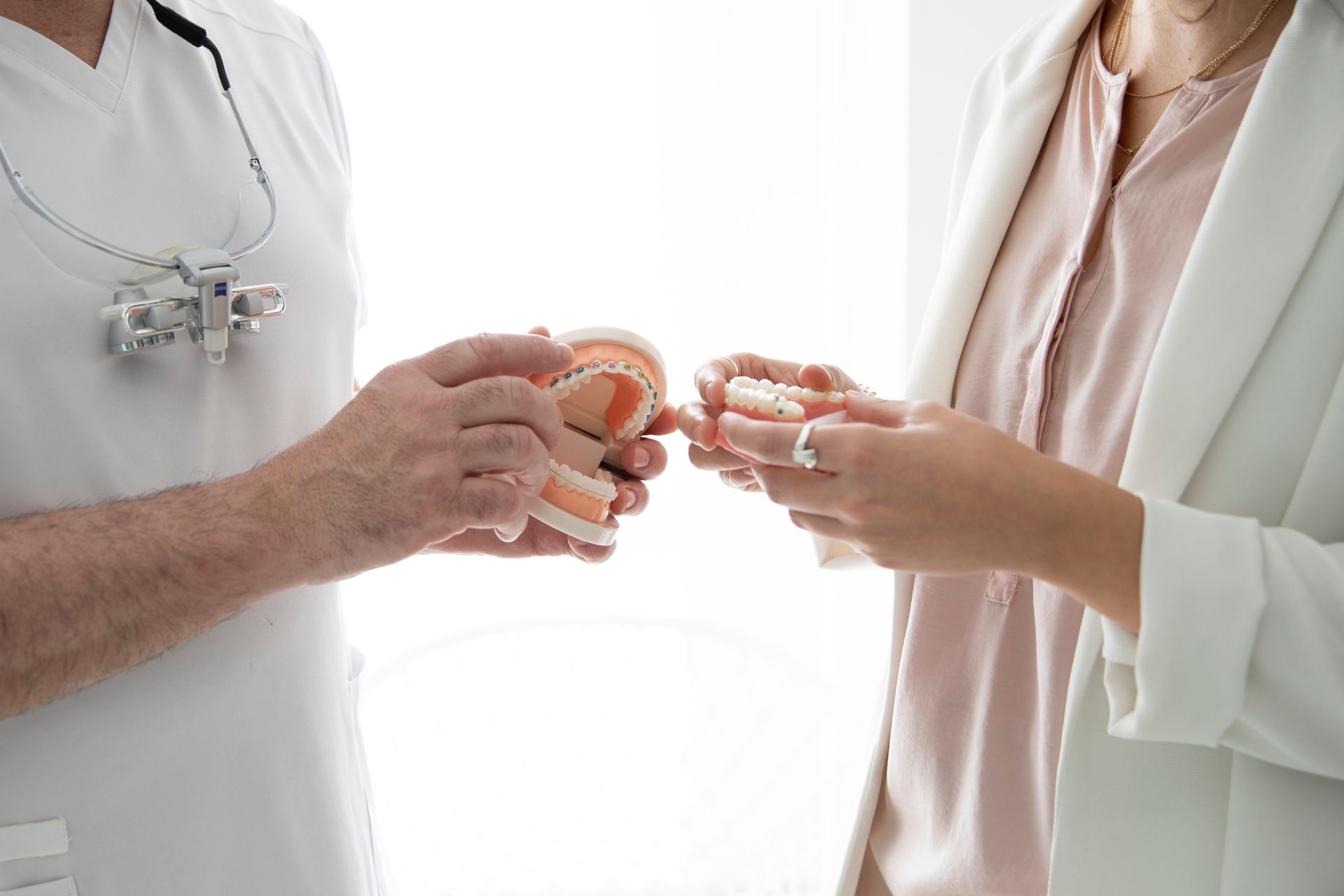
An orthodontist will thoroughly examine the teeth and jaws to determine the severity of the misalignment and develop a treatment plan. They may also take X-rays to better look at the underlying bone structure.
An orthodontist can diagnose four main malocclusions: overbite, underbite, open bite, and crossbite. Discover more about them:
- Overbite: This occurs the upper teeth overlap the lower teeth too much.
- Underbite: This happens when the lower teeth protrude past the upper teeth.
- Open bite: This results when a space exists between the biting surfaces of the front teeth when the back teeth are touching.
- Crossbite: This occurs when the upper and lower teeth do not line up correctly when biting down.
Children at Risk
Children who still suck their thumb at the age of five are at higher risk to develop pediatric malocclusion. Children with small spaces between their teeth may develop the disorder when they lose their milk teeth and grow permanent teeth. The small spaces obstruct good growth since permanent teeth need more space than milk ones.
Treatments
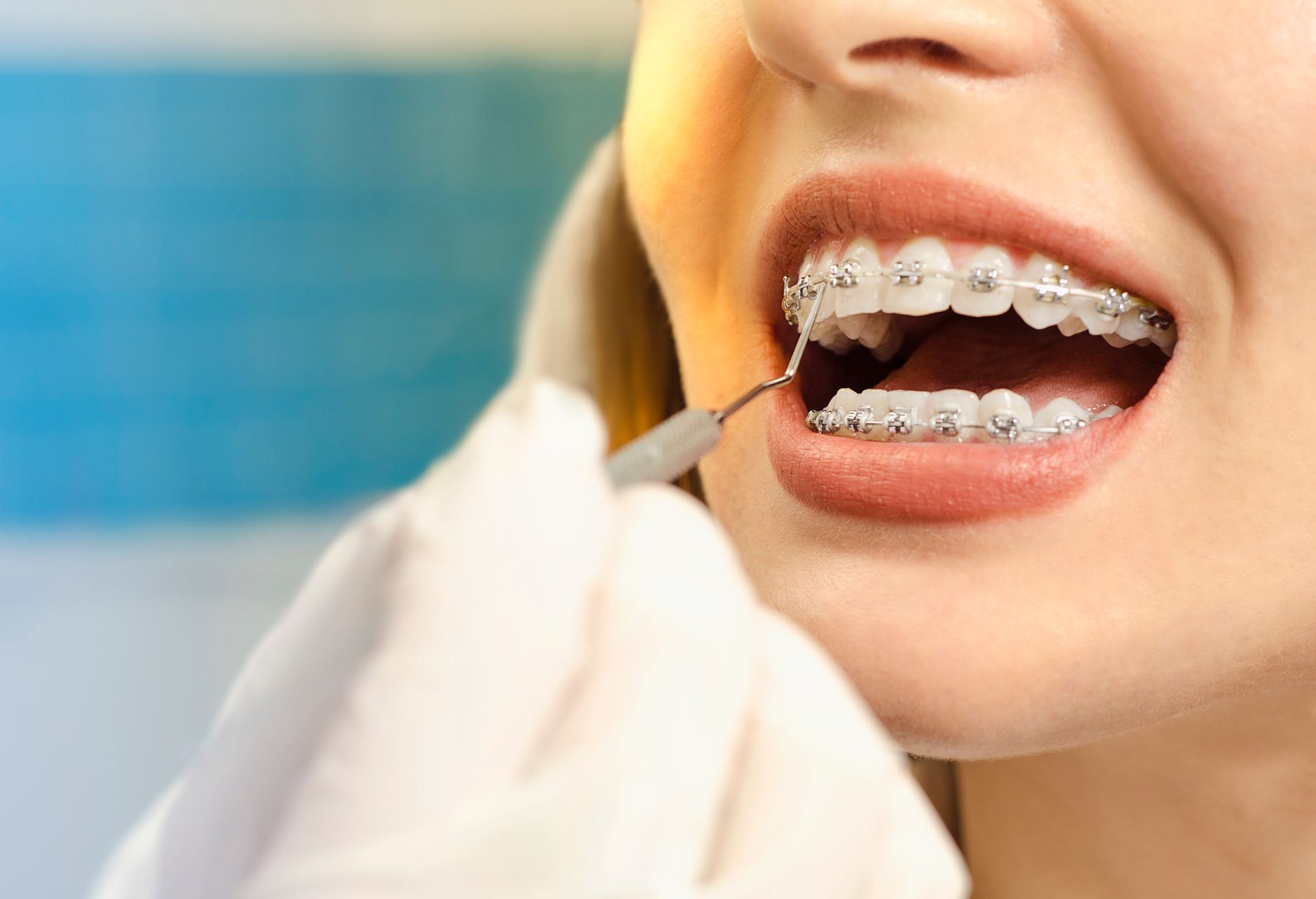
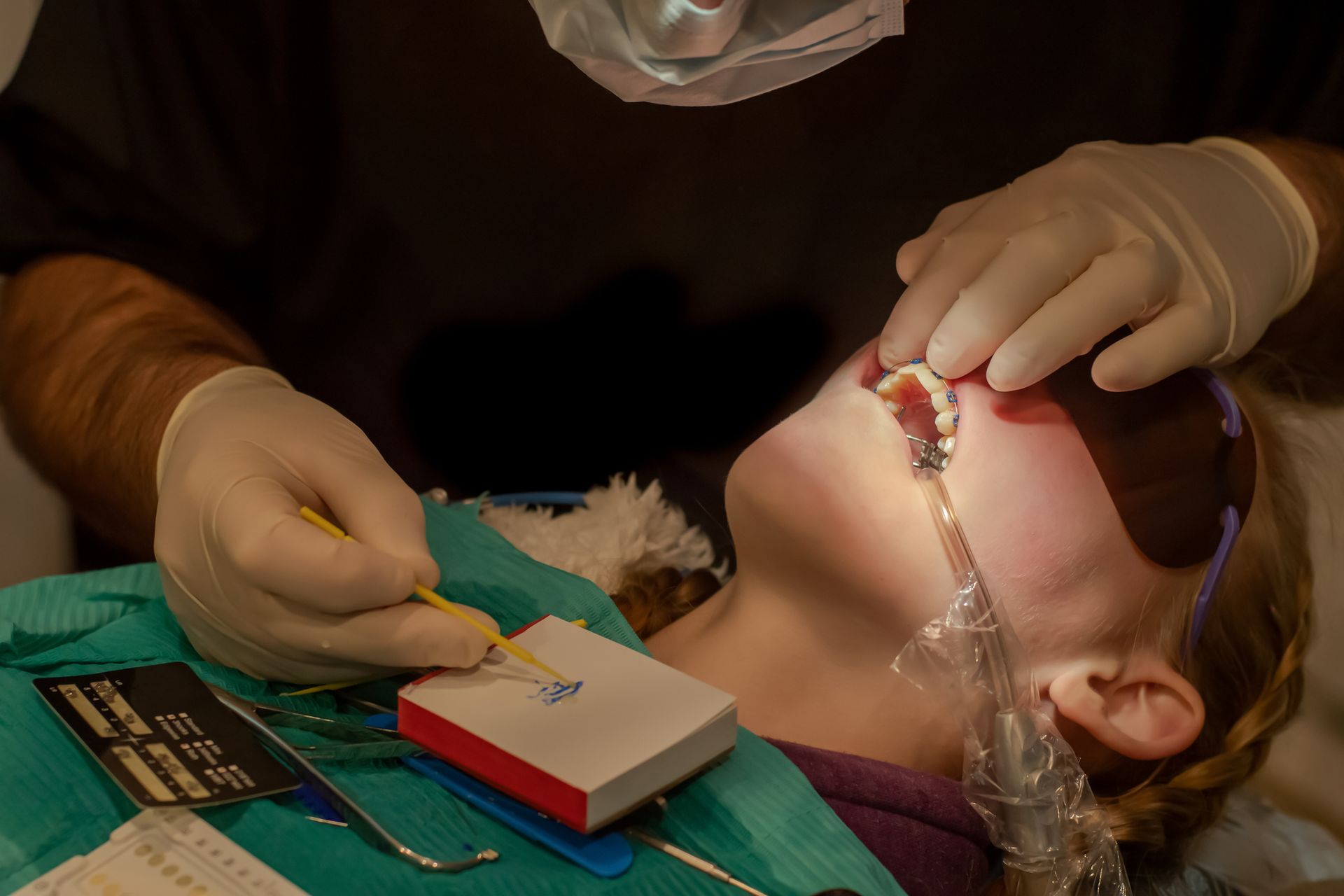
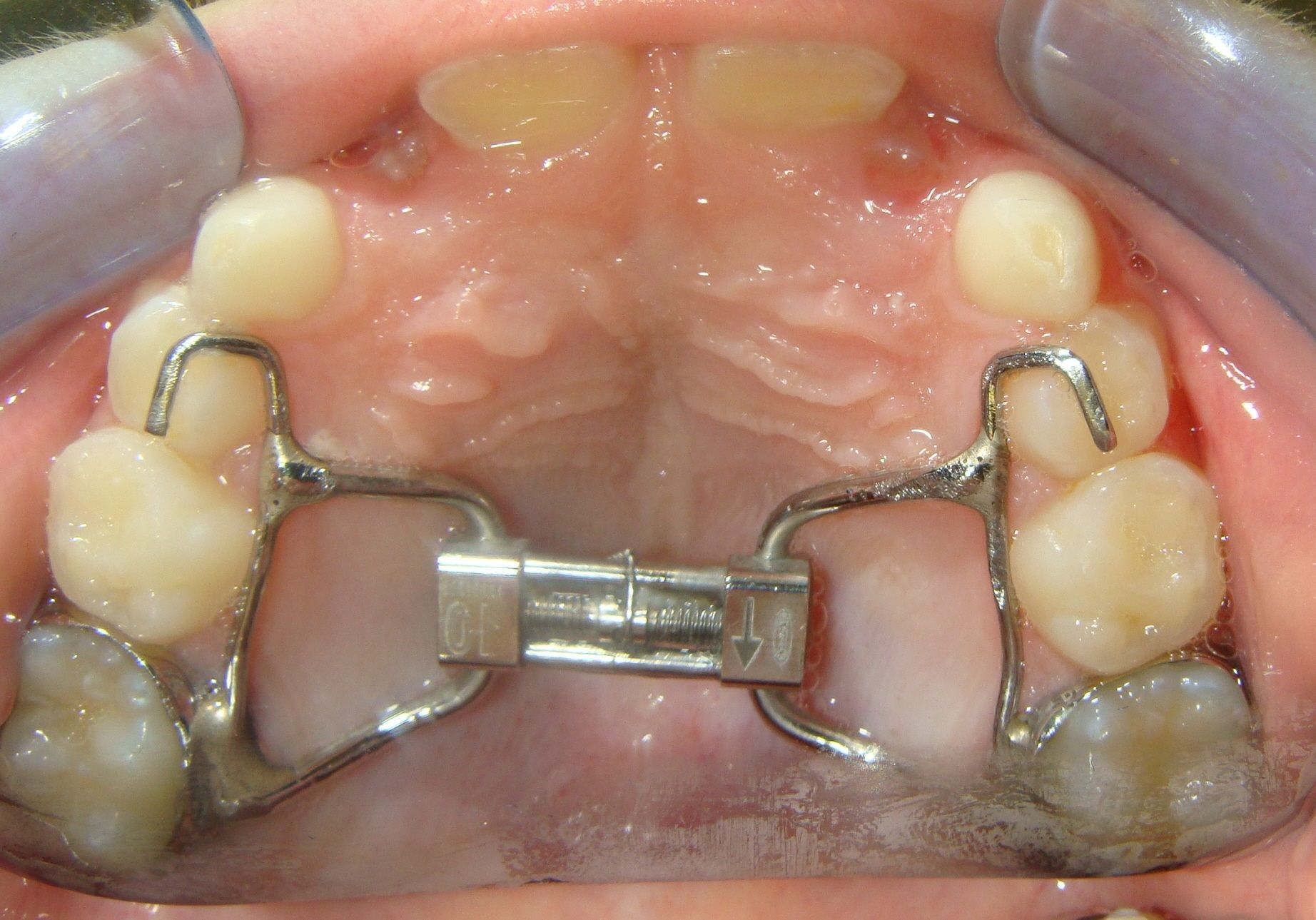
An orthodontist can treat malocclusion with braces that attach to the teeth and gradually move them into the correct position. The type of braces an orthodontist uses to treat a pediatric malocclusion will vary depending on the severity of the issue. For milder cases, they may use traditional metal braces. For more severe cases, they may use ceramic braces or even surgery.
Treatment Efficiency
The treatment efficiency of braces for pediatric malocclusion is typically very good. In most cases, the braces can correct the alignment of the teeth and jaws within a few months to a year. In some cases, however, the treatment may take longer.
Treatment Limitations
The treatment limitations for pediatric malocclusion are that it is often a slow process and that the child's mouth may not be big enough to accommodate all necessary dental work. Additionally, the child's bones may still develop, which makes it difficult to achieve the desired results.
Children who receive braces may have to limit their food to ensure the braces remain intact. Sticky and hard foods like gum, nuts, popcorn, and ice may reduce the efficiency of the treatment method.
Pediatric malocclusion is a treatable dental disorder that will require early intervention to ensure the treatment methods work as fast and efficiently as possible. Therefore, consult an orthodontist if you see some of the symptoms mentioned above to get a more detailed examination.
Visit us at Rosen Orthodontics to receive a full examination and treatment plan for potential dental disorders. We offer various interventions for malocclusion in children that can comfortably treat their condition.